Fission Reactor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
[[File:Fission reactor.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:Fission reactor.png|thumb|right]] | ||
A '''Fission Reactor''' is a multiblock structure that generates massive amounts of heat. How much heat is generated depends on the rate at which it burns [[Fissile Fuel]]. The only way to transform this heat into power is to inject "fresh" coolant into the reactor and use the heated coolant that comes out to generate power. Possible coolants are water and [[Sodium]]. With water cooled reactors, power is generated by directly piping steam into an [[Industrial Turbine]]. Sodium cooled reactors use a [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] as a heat-exchanger to cool down the [[Superheated sodium]] and heat up water into [[Steam]] that is in turn sent to an [[Industrial Turbine]]. | A '''Fission Reactor''' is a multiblock structure that generates massive amounts of heat. How much heat is generated depends on the rate at which it burns [[Fissile Fuel]]. The only way to transform this heat into power is to inject "fresh" coolant into the reactor and use the heated coolant that comes out to generate power. Possible coolants are water and [[Sodium]]. With water cooled reactors, power is generated by directly piping steam into an [[Industrial Turbine]]. Sodium cooled reactors use a [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] as a heat-exchanger to cool down the [[Superheated sodium]] and heat up water into [[Steam]] that is in turn sent to an [[Industrial Turbine]]. | ||
Fission reactors need special care: even at very low burn rates, they generate heat | Fission reactors need special care: even at very low burn rates, they generate heat faster than they can dissipate it to the environment. The biggest problem most players will face will be to maintain a steady flow of coolant. | ||
== Construction == | == Construction == | ||
| Line 60: | Line 58: | ||
The heating rate represents how much coolant is heated up per tick. The actual value depends on the burn rate. For a burn rate of one 1 mB/t, the heating rate is: | The heating rate represents how much coolant is heated up per tick. The actual value depends on the burn rate. For a burn rate of one 1 mB/t, the heating rate is: | ||
* | * 20,000 mB/t for a water cooled reactor | ||
* | * 200,000 mB/t for a sodium cooled reactor | ||
For safe operation, the external cooling setup must be able to handle that much heated coolant per tick. See [[ | For safe operation, the external cooling setup must be able to handle that much heated coolant per tick. See the [[#Water based cooling]] and [[#Sodium based cooling]] sections for more information. | ||
=== Temperature === | === Temperature === | ||
The core's temperature: green | The core's temperature: green (< 600K): optimal, yellow (>600K <1000K): getting hot, orange (>1000K <1200K): experts only, red (>1200K): the reactor is taking structural damage and will meltdown soon. | ||
=== Damage === | === Damage === | ||
This indicates the actual structural damage of the reactor. When a reactor reaches critical temperature, it will start taking damage and this value will go up. The damage value of a reactor that has overheated but been stopped on time to prevent a meltdown will slowly go down on its own, no player intervention is needed. | This indicates the actual structural damage of the reactor. When a reactor reaches critical temperature, it will start taking damage and this value will go up. The damage value of a reactor that has overheated but been stopped on time to prevent a meltdown will slowly go down on its own, no player intervention is needed. | ||
== Cooling and power production == | == Cooling and power production == | ||
Cooling a fission rector and converting the generated heat into power can be done in two ways: water cooling and sodium based cooling. | Cooling a fission rector and converting the generated heat into power can be done in two ways: water cooling and sodium based cooling. Regardless of the cooling solution, an [[Industrial Turbine]] will be the actual power generator. | ||
'''Important''': | '''Important''' (this applies to both cooling solutions): | ||
* the [[Industrial Turbine]] must have [[Saturating Condenser]]s in order to be able to condense steam into water and pipe that water back to the reactor | * the [[Industrial Turbine]] must have [[Saturating Condenser]]s in order to be able to condense steam into water and pipe that water back to the reactor cooling loop. The max water output from a turbine can be seen in its statistics tab. The actual value is 64000 mB of water per condenser. Condensers must be placed at the same level as the [[Electromagnetic Coil]]s or above them (a single coil being enough for 4 blades, this leaves plenty of room at the same level). | ||
* the turbine has an internal energy buffer that will slowly (more or less) fill up. Once full, it will only consume as much steam | * the turbine has an internal energy buffer that will slowly (more or less) fill up. Once full, it will only consume as much steam is needed to provide power to external consumers. As a result, its steam tank will start to fill up if the reactor generates steam faster than the turbine consumes it, less coolant will flow back to the reactor, resulting in less and less fresh coolant in the reactor's coolant tank. The reactor will start to eat up, until meltdown. See the [[#Safe operation]] section for more details and ways around this. | ||
=== Water based cooling === | === Water based cooling === | ||
[[File:Minimal fission reactor.png|thumb|right|Minimal water cooled fission reactor]] | [[File:Minimal fission reactor.png|thumb|right|Minimal water cooled fission reactor]] | ||
Water based cooling is sufficient for small setups | Water based cooling is sufficient for small setups. The actual limit is for reactors with about 75 [[Fission Fuel Assembly]]. It might be possible to go higher since larger reactors run cooler than smaller ones, but the temperature of such a reactor will be above 850K, well into the warning zone. Water cooling is ideal for players who want to start with a small-ish setup to get their feet wet with nuclear fission, or those who just don't want to bother with sodium based cooling. | ||
==== Optimal turbine size vs. reactor size ==== | |||
A water cooled reactor has a heating rate of 20,000 mB of water for 1 mB of [[Fissile Fuel]] burnt. For your reactor to run smoothly, the turbine's max steam flow and max water output must be greater than the reactor's heating rate. The maximum steam flow can be seen on a turbine's main GUI, and the maximum water flow in the stats tab of the GUI. The [[Industrial Turbine]]'s wiki page gives precise instructions on how to calculate a turbine's maximum flow based on its size and number of vents. | |||
The math is pretty tedious, so just keep the following in mind: | |||
* The actual power generated per mB of [[Fissile Fuel]] depends on the number of rotor blades in the turbine. Nothing else. The actual value is 7.14 kJ per blade for 1 mB of fissile fuel. For best results, do not hesitate to build a huge turbine and power it with a tiny reactor. | |||
* The width of the base of the turbine only limits its rotor height (rotor height = (width * 2) - 5), not the total structure height (the [[Industrial Turbine]]'s wiki page implies otherwise). | |||
* The limiting factor for the fissile fuel burn rate will be the minimum value between the turbine's steam flow rate (which depends on turbine size and number of turbine vents) and water flow rate (which depends on the number of condensers fitted). If need be, additional layers of condensers can be added on top of the [[Electromagnetic Coils]] layer. | |||
Based on this, the best bang for the buck for a water cooled reactor will be a 5x9x5 turbine with a 5 blocks high rotor (10 blades), 3 coils, the rest of the coil layer fitted with 6 condensers, and a total of 33 vents. While this turbine has a max steam flow of 1,056,000 mB/t, the limiting factor here is the water flow rate: 6 condensers * 64,000 mB/t = 384,000 mB/t. The reactor's maximum burn rate will then be 384,000 / 20,000 = 19.2 mB/t which is roughly the upper limit of water cooling (running at 610 Kelvin, hot, but workable). This will generate a respectable 1.37 MJ/t of power. Also, vents may be expensive at this point for most players: 12 are enough for this setup (this will make the max steam flow rate equal to 384,000 mB/t, matching the water flow rate nicely). | |||
==== Setup ==== | ==== Setup ==== | ||
| Line 101: | Line 106: | ||
The pipes and tubes connecting the reactor and turbine must have a [[Throughput]] at least equal to the heating rate of the reactor. See also [[#Safe operation]]. As mentioned above, the power drain must be higher than what the turbine actually produces (use an [[Induction Matrix]] between the turbine and the rest of the power consumers. Monitor the matrix's fill ratio regularly. | |||
==== Sample build ==== | ==== Sample build ==== | ||
The picture to the right shows a minimal fission reactor setup. From left to right: [[Induction Matrix]], [[Industrial Turbine]], Fission Reactor. The reactor has a single [[Fission Fuel Assembly]]. It takes [[Fissile Fuel]] from its front input port, [[Nuclear Waste]] is output to the right to a [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]]. In the back behind the reactor, there are two [[Electric Pump]]s feeding the coolant loop with fresh water | The picture to the right shows a minimal fission reactor setup. From left to right: [[Induction Matrix]], [[Industrial Turbine]], Fission Reactor. The reactor has a single [[Fission Fuel Assembly]]. It takes [[Fissile Fuel]] from its front input port, [[Nuclear Waste]] is output to the right to a [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]]. In the back behind the reactor, there are two [[Electric Pump]]s feeding the coolant loop with fresh water. The [[Industrial Turbine]] is the 5x9x5 described above. This setup generates 71.4 kJ/t when burning [[Fissile Fuel]] at its maximum of 1 mB/t. That's roughly 2.5 times less power than a [[Gas-Burning Generator]] burning [[Ethylene]]. | ||
=== Sodium based cooling === | === Sodium based cooling === | ||
| Line 114: | Line 117: | ||
[[File:Sodium cooled reactor (back).png|thumb|right|Boiler - Turbine piping]] | [[File:Sodium cooled reactor (back).png|thumb|right|Boiler - Turbine piping]] | ||
When things get too hot for your taste, [[Sodium]] is a much more efficient coolant and allows very high burn rates at lower core temperatures (but not more energy per mB of fuel burnt). [[Sodium]] based cooling requires a [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] as an intermediate heat-exchanger to cool down the [[Superheated sodium]] from the reactor and heat up water into [[Steam]]. | |||
The [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] has been updated in Makanism v10 to allow it to use heated coolant as a heat source. The boiler's water and steam tanks double as superheated coolant and coolant tanks. The [[Boiler Valve]]s can be configured with a [[Configurator]] (crouch + right click) to make them input only, output steam or output coolant. | The [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] has been updated in Makanism v10 to allow it to use heated coolant as a heat source. The boiler's water and steam tanks double as superheated coolant and coolant tanks. The [[Boiler Valve]]s can be configured with a [[Configurator]] (crouch + right click) to make them input only, output steam or output coolant. | ||
==== Optimal turbine size and boiler size vs. reactor size ==== | |||
With sodium cooling, the reactor will heat 200,000 of sodium per tick per mB of fissile fuel burnt. However, on the turbine's side, the steam and water flow rate requirements will be the same as in the water cooling scenario: 20,000 mB of steam/water per mB of Fissile Fuel. When sizing the turbine, just keep this in mind mind and use either 20,000*reactor_burn_rate or reactor_heating_rate/10. | |||
The size of the boiler will depend on the desired tank sizes and boil rate. | |||
Boilers have four tanks: heated coolant, water, steam and (cold) coolant. Compared to a Mekanism v9 boiler, in v10 the water tank doubles as a heated coolant tank and the steam tank doubles as a coolant tank. The water tank capacities are: | |||
* Water tank: external volume of the boiler from its base (included) to the topmost cavity layer, minus the number of [[Superheating Elements]], multiplied by 16,000 mB. | |||
* Heated coolant tank: 16 times the size of the water tank | |||
* Steam tank: external volume of the boiler from the steam catch layer up to the topmost steam cavity layer multiplied by 160,000 mB. The volume includes the [[Pressure Disperser]]s, but not the topmost layer of the boiler casing. | |||
* Coolant tank: volume of the steam tank times 1.6 | |||
A boiler's maximum boil rate (its boil capacity) is determined by the number of installed [[Superheating Element]]s. Each element contributes 320,000 mB/t to the boiler's boil capacity. The heating layer does not have to be full of superheating elements, you can install just as meany as needed such that the boiler's boil capacity greater or equal than the turbine's max steam and water flow. This will leave that much more room for the water and heated coolant. | |||
Evaluating the boiler size is more complex. Also, to answer the question how big can make it here and now: a maximum size reactor (18x18x18) needs two boilers to run at above 800 mB/t burn rate and three steam turbines. It reaches its maximum at about 1400 mB/t where it reaches the maximum operating temperature of 1200 K. | |||
For example with a 5x18x5 reactor (75 fuel assemblies), the boiler's heated coolant tank size must be about twice the size of the reactor's coolant tank (5*18*5 * 100,000 = 5,000,000 mB). With as much coolant buffered in the coolant return tube and as much water as the water tank's capacity buffered in the water return tubes, the reactor can be started at its maximum capacity without issues. This is a good starting point for small to mid size reactors. Again, start with low burn rates, wait the temperature and all tank levels to stabilize and increase the burn rate gradually. | |||
==== Setup ==== | ==== Setup ==== | ||
| Line 126: | Line 147: | ||
Next, connect the the boiler steam output (at or above the steam catch layer) to the turbine steam input, and pipe water back from one of the turbine's vents to one of the boiler's inputs at the heater or water cavity layers. | Next, connect the the boiler steam output (at or above the steam catch layer) to the turbine steam input, and pipe water back from one of the turbine's vents to one of the boiler's inputs at the heater or water cavity layers. | ||
Setup some fully upgraded [[Electric Pump]]s (1 KJ/t for 1000 mB of water per tick) to inject fresh water into the water-steam loop. It is necessary to keep them running in order to keep the boiler's water tank full when running at high heating rates | Setup some fully upgraded [[Electric Pump]]s (1 KJ/t for 1000 mB of water per tick) to inject fresh water into the water-steam loop. It is necessary to keep them running in order to keep the boiler's water tank full when running at high heating rates. How many pumps are required is left to the reader to experiment with (see [[#Safe Operation]]). | ||
For the reactor itself: | For the reactor itself: | ||
| Line 133: | Line 154: | ||
* Connect the boiler's coolant output to one of the reactor's inputs. While the boiler's valves must be placed in the proper layers. the placement of the reactor ports does not matter. | * Connect the boiler's coolant output to one of the reactor's inputs. While the boiler's valves must be placed in the proper layers. the placement of the reactor ports does not matter. | ||
* Connect a [[Fission Reactor Port]] configured as waste output to the top or bottom side of [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]] with a [[Pressurized Tube]] | * Connect a [[Fission Reactor Port]] configured as waste output to the top or bottom side of [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]] with a [[Pressurized Tube]] | ||
For your reactor to run smoothly, the tubes connecting the reactor and boiler must have a [[Throughput]] greater than the heating rate of the reactor, and the tubes and pipes running between the boiler and turbine must be grater than the boiler's boil capacity (this can be seen in the boiler's stats tab). | For your reactor to run smoothly, the tubes connecting the reactor and boiler must have a [[Throughput]] greater than the heating rate of the reactor, and the tubes and pipes running between the boiler and turbine must be grater than the boiler's boil capacity (this can be seen in the boiler's stats tab). | ||
| Line 155: | Line 173: | ||
* For good measure, even if a tube or pipe just crosses a chunk, keep it loaded. | * For good measure, even if a tube or pipe just crosses a chunk, keep it loaded. | ||
* Always start with low burn rates (the default 0.1 mB/t is good!) and increase it in small steps. | * Always start with low burn rates (the default 0.1 mB/t is good!) and increase it in small steps. | ||
* Use conservative on burn rates. Even the biggest reactor backed by several boilers and turbines cannot | * Use conservative on burn rates. Even the biggest reactor backed by several boilers and turbines cannot be started full blast and even less at its maximum theoretical burn rate. | ||
* Read the [[Throughput]] page and double check that throughput of the cables, pipes and tubes connecting the different components of your system is sufficient compared to the heating, boiling and flow rates. | |||
* The water flow rate of the turbine is easy to overlook. It can be checked in the turbine's stats tab and must be greater than the reactor's heating rate for water cooling and 1/10th of it for sodium cooling. | |||
| Line 181: | Line 201: | ||
Note that this should be used to switch off the reactor if the waste tanks gets full. This is just not fast enough. A redstone comparator on a waste barrel used as buffer on the reactor's waste output is a much better solution. | Note that this should be used to switch off the reactor if the waste tanks gets full. This is just not fast enough. A redstone comparator on a waste barrel used as buffer on the reactor's waste output is a much better solution. | ||
=== Troubleshooting | === Troubleshooting === | ||
Bottlenecks in the cooling chain and power drain are what limits the actual burn rate of a reactor. | Bottlenecks in the cooling chain and power drain are what limits the actual burn rate of a reactor. | ||
The reactor must have sufficient coolant before starting it and its heated coolant tank must be empty (a non empty tank means that you have excess coolant in the system). Players who will go straight for a sodium based solution may not have yet enough sodium to fully fill the coolant tank. Even at 10% full, the reactor can still be used, just keep the burn rate low enough to always have some fresh coolant in the reactor while it is running. | The reactor must have sufficient coolant before starting it and its heated coolant tank must be empty (a non empty tank means that you have excess coolant in the system). Players who will go straight for a sodium based solution may not have yet enough sodium to fully fill the coolant tank. Even at 10% full, the reactor can still be used, just keep the burn rate low enough to always have some fresh coolant in the reactor while it is running. | ||
Make sure that the [[Throughput]] of the pipe or tube networks for the coolant is greater than the heating rate. | |||
Make sure that the [[Throughput]] of the pipe or tube networks for the coolant is greater than the heating rate | |||
Again, start with low burn rates (< 1 mB/tick) and wait for the reactor heat to stabilize. If the heat indicator turns yellow (> 600K), the reactor is running too hot (experts can push it well into the "orange zone" at 1 to 1.2K but... here be dragons). When it turns orange or red, it's time to hit the SCRAM button (and check that your circuit breaker is working). The same applies if coolant tank fills suddenly and the temperature goes up rapidly. SCRAM! Also check that the heated coolant and water levels in the boiler are stable as well as the steam level in the turbine. | |||
When activating a reactor, some of its coolant immediately moves to the boiler as heated coolant, and some of the boiler's water moves to the turbine as steam. Having enough coolant buffered in the coolant tubes will compensate for this. As for water, you should always have several pumps ton compensate quickly. How quickly depends on how fast it drops when starting the reactor. If looking at the GUI of the boiler, the water level drops below that of the heated coolant, this is a sign that you have not enough water supply and that your boiler tank might not be large enough. | |||
Again, an [[Industrial Turbine]] must be fitted with enough [[Saturating Condenser]]s to allow a sufficient flow of water back from the turbine to the reactor or [[Thermoelectric Boiler]]. 1 mB/t of [[Fissile fuel]] burnt requires 20000 mB/t of steam and water (this applies to water and sodium cooled reactors). Given that a condenser provides 64000 mB/t of water, this translates to 1 condenser for 3.2 mB/t of [[Fissile Fuel]] burnt. | |||
The turbine also has an internal power storage (the gauge to the right of its GUI). When this fills up, this is a sign that there is not enough power drain in the system. If you let it reach its maximum, the turbine will stop consuming steam and sending water back into the cooling loop, resulting in a catastrophic meltdown. A solution around this is to: | |||
* install an induction matrix between your turbine and the rest of your base. A small matrix will do: build a 4x3x4 casing (the faces can be structural glass), install a basic provider and cell, this will give you room for two more cell and let you upgrade your cells as you get the resources to do so. The matrix GUI will give you a good view of how much power is produced and consumed at a glance. | |||
* Tune the reactor burn rate to be slightly above your average power usage. | |||
* Check the matrix time to time. If it gets full, pop in another cell or upgrade the ones already in it. Or just deactivate the reactor and let the matrix drain. | |||
== Radiation and nuclear waste handling == | == Radiation and nuclear waste handling == | ||
Revision as of 03:35, 25 July 2020

A Fission Reactor is a multiblock structure that generates massive amounts of heat. How much heat is generated depends on the rate at which it burns Fissile Fuel. The only way to transform this heat into power is to inject "fresh" coolant into the reactor and use the heated coolant that comes out to generate power. Possible coolants are water and Sodium. With water cooled reactors, power is generated by directly piping steam into an Industrial Turbine. Sodium cooled reactors use a Thermoelectric Boiler as a heat-exchanger to cool down the Superheated sodium and heat up water into Steam that is in turn sent to an Industrial Turbine.
Fission reactors need special care: even at very low burn rates, they generate heat faster than they can dissipate it to the environment. The biggest problem most players will face will be to maintain a steady flow of coolant.
Contents
Construction
- The structure must be a cuboid of minimum size 3x4x3 (along X, Y and Z), up to 18x18x18.
- The edges of the outer shell must be made of Fission Reactor Casing
- The faces of the outer shell can be either Fission Reactor Casing, Reactor Glass, Fission Reactor Port or Fission Reactor Logic Adapter
- The interior of the cube can be either air or fission control rods:
- A control rod is formed by a 1x1 block wide column made of 1 to 15 Fission Fuel Assembly and a single Control Assembly at the top
- Control rods must not touch each other. Maximum control rod density can be achieved by placing them in a checkerboard pattern.
Some example control rod setups as seen from the top ( is for Fission Reactor Casing or Reactor Glass, R is for a control rod):
CCCCC CCCCC
CCC C C CR RC
CRC CR RC C R C
CCC C C CR RC
CCCCC CCCCC
A fission reactor requires at least 4 Fission Reactor Ports:
- One coolant input
- One coolant output
- One Fissile Fuel input
- One waste output
Output ports must be configured to the proper output type by crouching and right-clicking them with a Configurator.
Reactor GUI
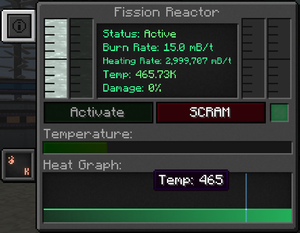
The reactor's GUI shows it's status, burn rate, heating rate, temperature and structural damage (health).
Status
The reactor's running status, either active or disabled.
To activate the reactor, either click the green activation button, or send a redstone signal to a Fission Reactor Logic Adapter configured in activation mode (just right click the Fission Reactor Logic Adapter block to configure it).
The reactor stops when a player clicks the red SCRAM button or if a redstone signal on a logic adapter goes from 1 to 0.
Burn Rate
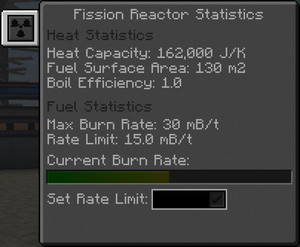
The burn rate is the rate at which the reactor will burn Fissile Fuel. For a newly formed reactor, it is automatically set to 0.1 mB/t. It can be changed in the reactor's statistics tab.
The theoretical maximum burn rate is 1 mB/t per [[Fission Fuel Assembly in the reactor, but the effective maximum burn rate depends on a number of factors (see #Safe operation).
Heating Rate
The heating rate represents how much coolant is heated up per tick. The actual value depends on the burn rate. For a burn rate of one 1 mB/t, the heating rate is:
- 20,000 mB/t for a water cooled reactor
- 200,000 mB/t for a sodium cooled reactor
For safe operation, the external cooling setup must be able to handle that much heated coolant per tick. See the #Water based cooling and #Sodium based cooling sections for more information.
Temperature
The core's temperature: green (< 600K): optimal, yellow (>600K <1000K): getting hot, orange (>1000K <1200K): experts only, red (>1200K): the reactor is taking structural damage and will meltdown soon.
Damage
This indicates the actual structural damage of the reactor. When a reactor reaches critical temperature, it will start taking damage and this value will go up. The damage value of a reactor that has overheated but been stopped on time to prevent a meltdown will slowly go down on its own, no player intervention is needed.
Cooling and power production
Cooling a fission rector and converting the generated heat into power can be done in two ways: water cooling and sodium based cooling. Regardless of the cooling solution, an Industrial Turbine will be the actual power generator.
Important (this applies to both cooling solutions):
- the Industrial Turbine must have Saturating Condensers in order to be able to condense steam into water and pipe that water back to the reactor cooling loop. The max water output from a turbine can be seen in its statistics tab. The actual value is 64000 mB of water per condenser. Condensers must be placed at the same level as the Electromagnetic Coils or above them (a single coil being enough for 4 blades, this leaves plenty of room at the same level).
- the turbine has an internal energy buffer that will slowly (more or less) fill up. Once full, it will only consume as much steam is needed to provide power to external consumers. As a result, its steam tank will start to fill up if the reactor generates steam faster than the turbine consumes it, less coolant will flow back to the reactor, resulting in less and less fresh coolant in the reactor's coolant tank. The reactor will start to eat up, until meltdown. See the #Safe operation section for more details and ways around this.
Water based cooling
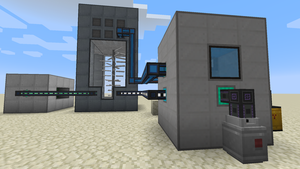
Water based cooling is sufficient for small setups. The actual limit is for reactors with about 75 Fission Fuel Assembly. It might be possible to go higher since larger reactors run cooler than smaller ones, but the temperature of such a reactor will be above 850K, well into the warning zone. Water cooling is ideal for players who want to start with a small-ish setup to get their feet wet with nuclear fission, or those who just don't want to bother with sodium based cooling.
Optimal turbine size vs. reactor size
A water cooled reactor has a heating rate of 20,000 mB of water for 1 mB of Fissile Fuel burnt. For your reactor to run smoothly, the turbine's max steam flow and max water output must be greater than the reactor's heating rate. The maximum steam flow can be seen on a turbine's main GUI, and the maximum water flow in the stats tab of the GUI. The Industrial Turbine's wiki page gives precise instructions on how to calculate a turbine's maximum flow based on its size and number of vents.
The math is pretty tedious, so just keep the following in mind:
- The actual power generated per mB of Fissile Fuel depends on the number of rotor blades in the turbine. Nothing else. The actual value is 7.14 kJ per blade for 1 mB of fissile fuel. For best results, do not hesitate to build a huge turbine and power it with a tiny reactor.
- The width of the base of the turbine only limits its rotor height (rotor height = (width * 2) - 5), not the total structure height (the Industrial Turbine's wiki page implies otherwise).
- The limiting factor for the fissile fuel burn rate will be the minimum value between the turbine's steam flow rate (which depends on turbine size and number of turbine vents) and water flow rate (which depends on the number of condensers fitted). If need be, additional layers of condensers can be added on top of the Electromagnetic Coils layer.
Based on this, the best bang for the buck for a water cooled reactor will be a 5x9x5 turbine with a 5 blocks high rotor (10 blades), 3 coils, the rest of the coil layer fitted with 6 condensers, and a total of 33 vents. While this turbine has a max steam flow of 1,056,000 mB/t, the limiting factor here is the water flow rate: 6 condensers * 64,000 mB/t = 384,000 mB/t. The reactor's maximum burn rate will then be 384,000 / 20,000 = 19.2 mB/t which is roughly the upper limit of water cooling (running at 610 Kelvin, hot, but workable). This will generate a respectable 1.37 MJ/t of power. Also, vents may be expensive at this point for most players: 12 are enough for this setup (this will make the max steam flow rate equal to 384,000 mB/t, matching the water flow rate nicely).
Setup
- Pump water into a Fission Rector Port configured as input only
- Connect a Fission Reactor Port configured as coolant output to the steam input valve of an Industrial Turbine.
- Connect a Mechanical Pipe from one of the Industrial Turbine's vents back to the coolant input of the reactor (or back to the same same mechanical pipe network from the first step).
- Connect a Fission Reactor Port configured as waste output to the top or bottom side of Nuclear Waste Barrel with a Pressurized Tube
The pipes and tubes connecting the reactor and turbine must have a Throughput at least equal to the heating rate of the reactor. See also #Safe operation. As mentioned above, the power drain must be higher than what the turbine actually produces (use an Induction Matrix between the turbine and the rest of the power consumers. Monitor the matrix's fill ratio regularly.
Sample build
The picture to the right shows a minimal fission reactor setup. From left to right: Induction Matrix, Industrial Turbine, Fission Reactor. The reactor has a single Fission Fuel Assembly. It takes Fissile Fuel from its front input port, Nuclear Waste is output to the right to a Nuclear Waste Barrel. In the back behind the reactor, there are two Electric Pumps feeding the coolant loop with fresh water. The Industrial Turbine is the 5x9x5 described above. This setup generates 71.4 kJ/t when burning Fissile Fuel at its maximum of 1 mB/t. That's roughly 2.5 times less power than a Gas-Burning Generator burning Ethylene.
Sodium based cooling


When things get too hot for your taste, Sodium is a much more efficient coolant and allows very high burn rates at lower core temperatures (but not more energy per mB of fuel burnt). Sodium based cooling requires a Thermoelectric Boiler as an intermediate heat-exchanger to cool down the Superheated sodium from the reactor and heat up water into Steam.
The Thermoelectric Boiler has been updated in Makanism v10 to allow it to use heated coolant as a heat source. The boiler's water and steam tanks double as superheated coolant and coolant tanks. The Boiler Valves can be configured with a Configurator (crouch + right click) to make them input only, output steam or output coolant.
Optimal turbine size and boiler size vs. reactor size
With sodium cooling, the reactor will heat 200,000 of sodium per tick per mB of fissile fuel burnt. However, on the turbine's side, the steam and water flow rate requirements will be the same as in the water cooling scenario: 20,000 mB of steam/water per mB of Fissile Fuel. When sizing the turbine, just keep this in mind mind and use either 20,000*reactor_burn_rate or reactor_heating_rate/10.
The size of the boiler will depend on the desired tank sizes and boil rate.
Boilers have four tanks: heated coolant, water, steam and (cold) coolant. Compared to a Mekanism v9 boiler, in v10 the water tank doubles as a heated coolant tank and the steam tank doubles as a coolant tank. The water tank capacities are:
- Water tank: external volume of the boiler from its base (included) to the topmost cavity layer, minus the number of Superheating Elements, multiplied by 16,000 mB.
- Heated coolant tank: 16 times the size of the water tank
- Steam tank: external volume of the boiler from the steam catch layer up to the topmost steam cavity layer multiplied by 160,000 mB. The volume includes the Pressure Dispersers, but not the topmost layer of the boiler casing.
- Coolant tank: volume of the steam tank times 1.6
A boiler's maximum boil rate (its boil capacity) is determined by the number of installed Superheating Elements. Each element contributes 320,000 mB/t to the boiler's boil capacity. The heating layer does not have to be full of superheating elements, you can install just as meany as needed such that the boiler's boil capacity greater or equal than the turbine's max steam and water flow. This will leave that much more room for the water and heated coolant.
Evaluating the boiler size is more complex. Also, to answer the question how big can make it here and now: a maximum size reactor (18x18x18) needs two boilers to run at above 800 mB/t burn rate and three steam turbines. It reaches its maximum at about 1400 mB/t where it reaches the maximum operating temperature of 1200 K.
For example with a 5x18x5 reactor (75 fuel assemblies), the boiler's heated coolant tank size must be about twice the size of the reactor's coolant tank (5*18*5 * 100,000 = 5,000,000 mB). With as much coolant buffered in the coolant return tube and as much water as the water tank's capacity buffered in the water return tubes, the reactor can be started at its maximum capacity without issues. This is a good starting point for small to mid size reactors. Again, start with low burn rates, wait the temperature and all tank levels to stabilize and increase the burn rate gradually.
Setup
Setup a Thermoelectric Boiler + Industrial Turbine as described on the boiler page with the exception that in step 7, you will need two Boiler valves on a steam catch or steam cavity layer, one for steam output, the other for coolant output.
It is important to build the boiler with water cavity layers (step 3c of the boiler's setup) in order to have a decent enough water + heated coolant storage capacity. The steam cavity layer is not really necessary here unless you have excess coolant in the system.
Next, connect the the boiler steam output (at or above the steam catch layer) to the turbine steam input, and pipe water back from one of the turbine's vents to one of the boiler's inputs at the heater or water cavity layers.
Setup some fully upgraded Electric Pumps (1 KJ/t for 1000 mB of water per tick) to inject fresh water into the water-steam loop. It is necessary to keep them running in order to keep the boiler's water tank full when running at high heating rates. How many pumps are required is left to the reader to experiment with (see #Safe Operation).
For the reactor itself:
- Connect the reactor's heated coolant output to one of the boiler's inputs at the heater or water cavity layers
- Connect the boiler's coolant output to one of the reactor's inputs. While the boiler's valves must be placed in the proper layers. the placement of the reactor ports does not matter.
- Connect a Fission Reactor Port configured as waste output to the top or bottom side of Nuclear Waste Barrel with a Pressurized Tube
For your reactor to run smoothly, the tubes connecting the reactor and boiler must have a Throughput greater than the heating rate of the reactor, and the tubes and pipes running between the boiler and turbine must be grater than the boiler's boil capacity (this can be seen in the boiler's stats tab).
Sample build
The picture to the right shows a 5x9x5 sodium cooled fission reactor, backed by a fairly small 5x7x5 Thermoelectric Boiler and a 7x13x7 turbine with 18 blades. It produces 3.85 MJ/t (1.54 MFE/t, 385.63 kEU/t) at peak burn rate (30 mB/t). Note that this same turbine could work with a reactor twice that size, but the boiler would need to be extended. On the right side of the reactor there is a crude, yet effective breaker-switch system (see #Safe Operation).
The second picture shows the boiler and turbine piping as well as a single pump (which is not enough for this configuration).
Safe operation
The worst thing that can happen is a core meltdown, which in Mekanism results in a big explosion. Big. Really big. Followed by lethal radiations over a 5 chunks radius (that's 80 blocks) that will last for several in-game weeks.
A few rules of thumb:
- In order to avoid chunk loading related glitches, do not build a fission reactor, Thermoelectric Boiler or Industrial Turbine on a chunk boundary.
- Keep all chunks involved in fission power generation and waste recycling loaded (use an Anchor Upgrade in Teleporters or Quantum Entangloporters).
- For good measure, even if a tube or pipe just crosses a chunk, keep it loaded.
- Always start with low burn rates (the default 0.1 mB/t is good!) and increase it in small steps.
- Use conservative on burn rates. Even the biggest reactor backed by several boilers and turbines cannot be started full blast and even less at its maximum theoretical burn rate.
- Read the Throughput page and double check that throughput of the cables, pipes and tubes connecting the different components of your system is sufficient compared to the heating, boiling and flow rates.
- The water flow rate of the turbine is easy to overlook. It can be checked in the turbine's stats tab and must be greater than the reactor's heating rate for water cooling and 1/10th of it for sodium cooling.
Circuit Breaker
Every reactor should have a circuit breaker that will, in many cases, prevent accidental meltdown. This can be done with redstone circuits like RS-latches or edge-detectors.

The picture to the right show a simple yet effective circuit breaker based on an edge detector.
The bottom Fission Reactor Logic Adapter is set to emit a redstone signal on high temperature. The top one is set to "activation". This will activate the reactor when it receives a redstone signal , and deactivate it whenever the signal switches off.
The piston is a regular piston with a sand or gravel block on top. The observer is facing towards the camera, sending its signal to the reactor adapter. The only issue when building this breaker it to place the observer correctly (and triple check that the adapter it will cover is set to "activation"!). The safest solution is to push it into place using a piston.
Whenever the bottom adapter will send a redstone signal, this will push the piston and gravel block, making the observer send a one redstone tick pulse to the reactor, activating it (and making it register that it is redstone activated) and deactivating it almost immediately. The redstone torch is not part of the circuit breaker itself (see below).
DISCLAIMER: A circuit breaker alone will not help in all situations. In case of reactor overheating with a large reactor and burn rate and critical coolant shortage, the temperature will have reached over 1400K before tripping the breaker. Without a quick injection of new coolant, the reactor will not cool down quickly enough and will keep taking structural damage until the unthinkable happens.
This is the purpose of the redstone torch and redstone-activated coolant tube on the right hand side. The tube comes from an dynamic tank used as emergency coolant storage. As long as the high temperature signal is on, the tube will inject fresh coolant from the emergency tank into the reactor, bringing its temperature down much faster.
Just like for real circuit breakers a test button can be installed just beneath the observer on the face of the reactor. Pushing it should trigger the piston and activate the reactor very briefly before deactivating it.
An alarm can also be installed by using the bottom block (the one supporting the redstone dust and torch) as the input of an RS-latch and wiring the alarm on the output of the latch.
Note that this should be used to switch off the reactor if the waste tanks gets full. This is just not fast enough. A redstone comparator on a waste barrel used as buffer on the reactor's waste output is a much better solution.
Troubleshooting
Bottlenecks in the cooling chain and power drain are what limits the actual burn rate of a reactor.
The reactor must have sufficient coolant before starting it and its heated coolant tank must be empty (a non empty tank means that you have excess coolant in the system). Players who will go straight for a sodium based solution may not have yet enough sodium to fully fill the coolant tank. Even at 10% full, the reactor can still be used, just keep the burn rate low enough to always have some fresh coolant in the reactor while it is running.
Make sure that the Throughput of the pipe or tube networks for the coolant is greater than the heating rate.
Again, start with low burn rates (< 1 mB/tick) and wait for the reactor heat to stabilize. If the heat indicator turns yellow (> 600K), the reactor is running too hot (experts can push it well into the "orange zone" at 1 to 1.2K but... here be dragons). When it turns orange or red, it's time to hit the SCRAM button (and check that your circuit breaker is working). The same applies if coolant tank fills suddenly and the temperature goes up rapidly. SCRAM! Also check that the heated coolant and water levels in the boiler are stable as well as the steam level in the turbine.
When activating a reactor, some of its coolant immediately moves to the boiler as heated coolant, and some of the boiler's water moves to the turbine as steam. Having enough coolant buffered in the coolant tubes will compensate for this. As for water, you should always have several pumps ton compensate quickly. How quickly depends on how fast it drops when starting the reactor. If looking at the GUI of the boiler, the water level drops below that of the heated coolant, this is a sign that you have not enough water supply and that your boiler tank might not be large enough.
Again, an Industrial Turbine must be fitted with enough Saturating Condensers to allow a sufficient flow of water back from the turbine to the reactor or Thermoelectric Boiler. 1 mB/t of Fissile fuel burnt requires 20000 mB/t of steam and water (this applies to water and sodium cooled reactors). Given that a condenser provides 64000 mB/t of water, this translates to 1 condenser for 3.2 mB/t of Fissile Fuel burnt.
The turbine also has an internal power storage (the gauge to the right of its GUI). When this fills up, this is a sign that there is not enough power drain in the system. If you let it reach its maximum, the turbine will stop consuming steam and sending water back into the cooling loop, resulting in a catastrophic meltdown. A solution around this is to:
- install an induction matrix between your turbine and the rest of your base. A small matrix will do: build a 4x3x4 casing (the faces can be structural glass), install a basic provider and cell, this will give you room for two more cell and let you upgrade your cells as you get the resources to do so. The matrix GUI will give you a good view of how much power is produced and consumed at a glance.
- Tune the reactor burn rate to be slightly above your average power usage.
- Check the matrix time to time. If it gets full, pop in another cell or upgrade the ones already in it. Or just deactivate the reactor and let the matrix drain.
Radiation and nuclear waste handling
As a byproduct of burning Fissile Fuel, fission reactors produce Nuclear Waste which can be converted in either Polonium Pellet or Plutonium Pellet. Both conversion paths produce Spent Nuclear Waste as a byproduct (at a ratio of 10:1), which must be stored in Radioactive Waste Barrels. Nuclear Waste or Spent Nuclear Waste can be piped into a Nuclear Waste Barrel from its top or bottom side with a Pressurized Tube.
- Nuclear Waste is radioactive.
- All products and intermediate products of converting Uranium Ore to Fissile Fuel are not radioactive, i.e. safe to handle.
- Intermediate products and byproducts of recycling Nuclear Waste are radioactive: Polonium, Plutonium and Spent Nuclear Waste.
- Plutonium Pellets and Polonium Pellets are not radioactive.
Radiation can leak into the environment for the following reasons:
- Fission reactor overheating leading to a core meltdown (actually blowing up).
- Fission reactor running with its waste tank full.
- Breaking any block containing radioactive materials. Most notably Pressurized Tubes and Radioactive Waste Barrels. This also applies to machines, like a Pressurized Reaction Chamber containing polonium for example. These can still be broken safely if they are somehow drained of their radioactive contents beforehand.
Quantum Entangloporters cannot handle radioactive materials. As a result, it is not possible to make Polonium Pellets with a reactor in the nether (since the Solar Neutron Activator, which is required to produce Polonium from Nuclear Waste needs direct sunlight) or have a reactor in the overworld and store waste in the nether.
Nuclear Waste Barrels
TODO: move this to its own page
Waste Barrels are used to store (or as buffer for) Nuclear Waste and Spent Nuclear Waste. They delete their contents at a rate of 1 mB per minute.
The player can check the storage status of Nuclear Waste Barrels by crouching and right-clicking it with an empty hand. Green radiation particles start to appear as a barrel fills up (these are just a rough visual indicator of a barrel's fill ratio, not actual radiations).
Waste barrels cannot be moved by any means (pistons, cardboard box, etc.). Also because barrels containing any radioactive waste cannot be broken safely, the only way to safely move a non empty barrel it transfer its contents to another barrel before breaking it. This can be done by connecting a Pressurized Tube to its top or bottom side in pull mode.
Even if Waste Barrels are blast resistant, but pressurized tubes carrying waste to them are not. As a rule of thumb, do not allow creepers wandering around a fission reactor or waste transformation or disposal units.
Tips
- For any given reactor burn rate, the more turbine blades, the more energy is produced per mB of Fissile Fuel. As a result, the bigger the turbine the better. Also it is best to max out the rotor height and make trade-offs on the vents/condensers count. With a slightly shorter rotor, one could add more condensers and achieve higher burn rates and total power produced, but at a higher cost in terms of power produced per mB of Fissile Fuel burnt.
- Experiment in a creative world! There, you can experiment with the console commands (the last one is just in case things go wrong, but don't be a chicken and abuse it!):
/mek build fission /mek build remove /mek radiation removeAll
- Whenever Polonium Pellets are not needed anymore, keep recycling Nuclear Waste into Plutonium -> Plutonium Pellets -> Reprocessed Fissile Fragments -> Fissile Fuel. In addition to decreasing the uranium ore consumption, this divides the storage capacity needs of nuclear waste by a factor of 10.


