Fission Reactor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | |||
[[File:Fission reactor.png|thumb|Fission Reactor]] | [[File:Fission reactor.png|thumb|Fission Reactor]] | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
The '''Fission Reactor''' is a multiblock structure that allows for variable input rates of [[Fissile Fuel]]. The reactor uses either [[Sodium]] or water as a coolant. Power is generated by converting the generated heat into power in an [[Industrial Turbine]]. With water cooled reactors, this is done by directly piping steam into an [[Industrial Turbine]]. Sodium cooled reactors use a [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] as a heat-exchanger to cool down the [[Superheated sodium]] and heat up water into [[Steam]]. | The '''Fission Reactor''' is a multiblock structure that allows for variable input rates of [[Fissile Fuel]]. The reactor uses either [[Sodium]] or water as a coolant. Power is generated by converting the generated heat into power in an [[Industrial Turbine]]. With water cooled reactors, this is done by directly piping steam into an [[Industrial Turbine]]. Sodium cooled reactors use a [[Thermoelectric Boiler]] as a heat-exchanger to cool down the [[Superheated sodium]] and heat up water into [[Steam]]. | ||
== Construction == | == Construction == | ||
* The structure must be a cuboid of minimum size 3x4x3, up to 18x18x18. | * The structure must be a cuboid of minimum size 3x4x3 (along X, Y and Z), up to 18x18x18. | ||
* The edges of the outer shell must be made of [[Fission Reactor Casing]] | * The edges of the outer shell must be made of [[Fission Reactor Casing]] | ||
* The faces of the outer shell can be either [[Fission Reactor Casing]], [[Reactor Glass]], [[Fission Reactor Port]] or [[Fission Reactor Logic Adapter]] | * The faces of the outer shell can be either [[Fission Reactor Casing]], [[Reactor Glass]], [[Fission Reactor Port]] or [[Fission Reactor Logic Adapter]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
[[File:Fission Reactor GUI.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:Fission Reactor GUI.png|thumb|right]] | ||
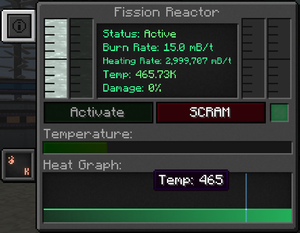
The reactor's GUI shows it's status | The reactor's GUI shows it's status, burn rate, heating rate, temperature and structural damage (health). | ||
=== Status === | === Status === | ||
The reactor's running status, either active or disabled. | |||
To activate the reactor, either click the green activation button, or send a redstone signal to a [[Fission Reactor Logic Adapter]] configured in activation mode (just right click the [[Fission Reactor Logic Adapter]] block to configure it). | |||
The reactor stops when a player clicks the red SCRAM button or if a redstone signal on a logic adapter goes from 1 to 0. | |||
=== Burn Rate === | === Burn Rate === | ||
| Line 47: | Line 52: | ||
[[File:Fission Reactor Stats.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:Fission Reactor Stats.png|thumb|right]] | ||
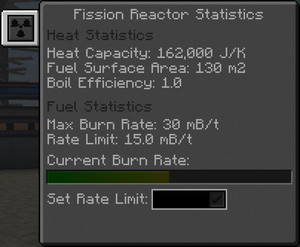
The burn rate is the rate at which the reactor will burn [[Fissile Fuel]]. For a newly formed reactor, it is automatically set to 0.1 mB/t. It can be changed in the reactor's statistics tab. | The burn rate is the rate at which the reactor will burn [[Fissile Fuel]]. For a newly formed reactor, it is automatically set to 0.1 mB/t. It can be changed in the reactor's statistics tab. | ||
The theoretical maximum burn rate is 1 mB/t per [[[[Fission Fuel Assembly]] in the reactor, but the effective maximum burn rate depends on a number of factors (see the safe operation section below). | |||
=== Heating Rate === | === Heating Rate === | ||
The heating rate represents how much coolant is heated up per tick. The actual value depends on the burn rate. For a burn rate of one 1 mB/t, the heating rate is: | |||
* 20000 mB/t for a water cooled reactor | |||
* 200000 mB/t for a sodium cooled reactor | |||
For safe operation, the external cooling setup must be able to handle that much heated coolant per tick. See the relevant section below. | |||
=== Temperature === | === Temperature === | ||
The core's temperature: green OK, yellow: danger zone, red: imminent meltdown. | |||
TODO: add actual figures. | |||
=== Damage === | === Damage === | ||
This indicates the actual structural damage of the reactor. When a reactor reaches critical temperature, it will start taking damage and this value will go up. The damage value of a reactor that has overheated but been stopped on time to prevent a meltdown will slowly go down on its own, no player intervention is needed. | |||
TODO: need more tech details: how fast is damage recovery? does it recover if running in the danger zone (yellow heat value), etc. | |||
== Cooling and power production == | == Cooling and power production == | ||
Cooling a fission rector and converting the generated heat into power can be done in two ways: water cooling and sodium based cooling. | |||
"Things to know" about how pipes/tubes work in Mekanism (to be moved into its own page): | |||
- The pump rate is the rate at which the pipe can pump gases/fluids from a container when set in pull mode | |||
- The capacity is how much the single pipe adds to to the pipe network's capacity (a pipe network being all pipes connected together) | |||
- At each tick, a pipe network tries to dump its whole buffer (i.e. up to the networks' capacity) evenly among all connected receivers | |||
- In effect, with no pipes set to pull mode, the actual transfer rate is limited by the minimum value of the providers ejection rate into the network and the network's capacity | |||
- If the ejection rate of a provider is lower than the pipe's rate, setting the pipe to pull mode will override the provider's ejection rate | |||
=== Water based cooling === | === Water based cooling === | ||
Water based cooling is sufficient for small setups, i.e. reactors with less than 20 [[Fission Fuel Assembly]] and a max burn rate of 20 mB/t. Beyond that, it gets hard to keep the reactor core temperature within acceptable parameters. | |||
Setup: | |||
* pipe water into a [[Fission Rector Port]] configured as input only | |||
* Connect a [[Fission Reactor Port]] configured as coolant output to the steam input valve of an [[Industrial Turbine]]. | |||
* Connect a [[Mechanical Pipe]] from one of the [[Industrial Turbine]]'s vents back to the coolant input of the reactor (or back to the same same mechanical pipe network from the first step). | |||
'''Important''': the [[Industrial Turbine]] must have [[Saturating Condenser]]s in order to be able to condense steam into water and pipe that water back to the reactor. The max water output from a turbine can be seen in its statistics tab. The actual value is 64000 mB of water per condenser. | |||
A water cooled reactor has a heat rate of 20000 mB of water for 1 mB of [[Fissile Fuel]] burnt. | |||
For any given reactor burn rate, the more turbine blades, the more energy is produced per mB of [[Fissile Fuel]]. As a result, the bigger the turbine the better. Also it is best to max out the rotor height and make trade-offs on the vents/condensers count. With a slightly shorter rotor, one could add more condensers and achieve higher burn rates and energy produced but at a higher cost in terms of power produced per mB of [[Fissile Fuel]]. | |||
=== Sodium based cooling === | === Sodium based cooling === | ||
'''Please read the water based cooling section first, even if you do not intend to implement it''' | |||
== Safe operation == | == Safe operation == | ||
| Line 65: | Line 111: | ||
=== Breaker switch === | === Breaker switch === | ||
== | |||
== Waste handling and radiation == | |||
As a byproduct of burning [[Fissile Fuel]], fission reactors produce [[Nuclear Waste]] which can be converted in either [[Polonium Pellet]] or [[Plutonium Pellet]]. Both conversion paths produce [[Spent Nuclear Waste]] as a byproduct (at a ratio of 10:1), which must be stored in [[Radioactive Waste Barrels]]. [[Nuclear Waste]] or [[Spent Nuclear Waste]] can be piped into a [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]] from its top side with a [[Pressurized Tube]]. | As a byproduct of burning [[Fissile Fuel]], fission reactors produce [[Nuclear Waste]] which can be converted in either [[Polonium Pellet]] or [[Plutonium Pellet]]. Both conversion paths produce [[Spent Nuclear Waste]] as a byproduct (at a ratio of 10:1), which must be stored in [[Radioactive Waste Barrels]]. [[Nuclear Waste]] or [[Spent Nuclear Waste]] can be piped into a [[Nuclear Waste Barrel]] from its top side with a [[Pressurized Tube]]. | ||
| Line 71: | Line 118: | ||
* [[Nuclear Waste]] is radioactive. | * [[Nuclear Waste]] is radioactive. | ||
* All products and intermediate products of converting [[Uranium Ore]] to [[Fissile Fuel]] are not radioactive, i.e. safe to handle. | * All products and intermediate products of converting [[Uranium Ore]] to [[Fissile Fuel]] are not radioactive, i.e. safe to handle. | ||
* Intermediate products of recycling [[Nuclear Waste]] are radioactive: [[Polonium]], [[Plutonium]] and [[Spent Nuclear Waste]]. | * Intermediate products and byproducts of recycling [[Nuclear Waste]] are radioactive: [[Polonium]], [[Plutonium]] and [[Spent Nuclear Waste]]. | ||
* [[Plutonium Pellet]]s and [[Polonium Pellet]]s are not radioactive. | * [[Plutonium Pellet]]s and [[Polonium Pellet]]s are not radioactive. | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 22 July 2020
This page is a work in progress! Many essential things are missing.
The Fission Reactor is a multiblock structure that allows for variable input rates of Fissile Fuel. The reactor uses either Sodium or water as a coolant. Power is generated by converting the generated heat into power in an Industrial Turbine. With water cooled reactors, this is done by directly piping steam into an Industrial Turbine. Sodium cooled reactors use a Thermoelectric Boiler as a heat-exchanger to cool down the Superheated sodium and heat up water into Steam.
Contents
Construction
- The structure must be a cuboid of minimum size 3x4x3 (along X, Y and Z), up to 18x18x18.
- The edges of the outer shell must be made of Fission Reactor Casing
- The faces of the outer shell can be either Fission Reactor Casing, Reactor Glass, Fission Reactor Port or Fission Reactor Logic Adapter
- The interior of the cube can be either air or fission control rods"
- A control rod is which are a 1x1 block wide column made of 1 to 15 Fission Fuel Assembly and a single Control Assembly at the top
- Control rods must not touch each other. The highest control rod density can be achieved by placing them in a checker board patters.
Some example control rod setups as seen from the top ( is for Fission Reactor Casing or Reactor Glass, R is for a control rod):
CCCCC CCCCC
CCC C C CR RC
CRC CR RC C R C
CCC C C CR RC
CCCCC CCCCC
A fission reactor requires at least 4 Fission Reactor Ports:
- One coolant input
- One coolant output
- One Fissile Fuel input
- One waste output
Output ports must be configured to the proper output type by right-clicking them with a Configurator.
Reactor GUI
The reactor's GUI shows it's status, burn rate, heating rate, temperature and structural damage (health).
Status
The reactor's running status, either active or disabled.
To activate the reactor, either click the green activation button, or send a redstone signal to a Fission Reactor Logic Adapter configured in activation mode (just right click the Fission Reactor Logic Adapter block to configure it).
The reactor stops when a player clicks the red SCRAM button or if a redstone signal on a logic adapter goes from 1 to 0.
Burn Rate
The burn rate is the rate at which the reactor will burn Fissile Fuel. For a newly formed reactor, it is automatically set to 0.1 mB/t. It can be changed in the reactor's statistics tab.
The theoretical maximum burn rate is 1 mB/t per [[Fission Fuel Assembly in the reactor, but the effective maximum burn rate depends on a number of factors (see the safe operation section below).
Heating Rate
The heating rate represents how much coolant is heated up per tick. The actual value depends on the burn rate. For a burn rate of one 1 mB/t, the heating rate is:
- 20000 mB/t for a water cooled reactor
- 200000 mB/t for a sodium cooled reactor
For safe operation, the external cooling setup must be able to handle that much heated coolant per tick. See the relevant section below.
Temperature
The core's temperature: green OK, yellow: danger zone, red: imminent meltdown.
TODO: add actual figures.
Damage
This indicates the actual structural damage of the reactor. When a reactor reaches critical temperature, it will start taking damage and this value will go up. The damage value of a reactor that has overheated but been stopped on time to prevent a meltdown will slowly go down on its own, no player intervention is needed.
TODO: need more tech details: how fast is damage recovery? does it recover if running in the danger zone (yellow heat value), etc.
Cooling and power production
Cooling a fission rector and converting the generated heat into power can be done in two ways: water cooling and sodium based cooling.
"Things to know" about how pipes/tubes work in Mekanism (to be moved into its own page):
- The pump rate is the rate at which the pipe can pump gases/fluids from a container when set in pull mode - The capacity is how much the single pipe adds to to the pipe network's capacity (a pipe network being all pipes connected together) - At each tick, a pipe network tries to dump its whole buffer (i.e. up to the networks' capacity) evenly among all connected receivers - In effect, with no pipes set to pull mode, the actual transfer rate is limited by the minimum value of the providers ejection rate into the network and the network's capacity - If the ejection rate of a provider is lower than the pipe's rate, setting the pipe to pull mode will override the provider's ejection rate
Water based cooling
Water based cooling is sufficient for small setups, i.e. reactors with less than 20 Fission Fuel Assembly and a max burn rate of 20 mB/t. Beyond that, it gets hard to keep the reactor core temperature within acceptable parameters.
Setup:
- pipe water into a Fission Rector Port configured as input only
- Connect a Fission Reactor Port configured as coolant output to the steam input valve of an Industrial Turbine.
- Connect a Mechanical Pipe from one of the Industrial Turbine's vents back to the coolant input of the reactor (or back to the same same mechanical pipe network from the first step).
Important: the Industrial Turbine must have Saturating Condensers in order to be able to condense steam into water and pipe that water back to the reactor. The max water output from a turbine can be seen in its statistics tab. The actual value is 64000 mB of water per condenser.
A water cooled reactor has a heat rate of 20000 mB of water for 1 mB of Fissile Fuel burnt.
For any given reactor burn rate, the more turbine blades, the more energy is produced per mB of Fissile Fuel. As a result, the bigger the turbine the better. Also it is best to max out the rotor height and make trade-offs on the vents/condensers count. With a slightly shorter rotor, one could add more condensers and achieve higher burn rates and energy produced but at a higher cost in terms of power produced per mB of Fissile Fuel.
Sodium based cooling
Please read the water based cooling section first, even if you do not intend to implement it
Safe operation
Breaker switch
Waste handling and radiation
As a byproduct of burning Fissile Fuel, fission reactors produce Nuclear Waste which can be converted in either Polonium Pellet or Plutonium Pellet. Both conversion paths produce Spent Nuclear Waste as a byproduct (at a ratio of 10:1), which must be stored in Radioactive Waste Barrels. Nuclear Waste or Spent Nuclear Waste can be piped into a Nuclear Waste Barrel from its top side with a Pressurized Tube.
- Nuclear Waste is radioactive.
- All products and intermediate products of converting Uranium Ore to Fissile Fuel are not radioactive, i.e. safe to handle.
- Intermediate products and byproducts of recycling Nuclear Waste are radioactive: Polonium, Plutonium and Spent Nuclear Waste.
- Plutonium Pellets and Polonium Pellets are not radioactive.
Radiation can leak into the environment for the following reasons:
- Fission reactor overheating leading to a core meltdown (actually blowing up).
- Fission reactor running with its waste tank full.
- Breaking any block containing radioactive materials. Most notably Pressurized Tubes and Radioactive Waste Barrels, but also any machine (like a Pressurized Reaction Chamber containing radioactive materials. These can still be broken safely if they are somehow drained of their radioactive contents beforehand.
The player can check the storage status of Nuclear Waste Barrels by crouching and right-clicking it with an empty hand. Green radiation particles start to appear as a barrel fills up (these are just a rough visual indicator of a barrel's fill ratio, not actual radiations).
While a barrel containing waste cannot be moved (because they cannot be broken safely in the first place), its contents can be drained from its bottom side with a tube in pull mode and moved to another barrel with a tube network. Once empty, the barrel can be safely broken.
Quantum Entangloporters cannot handle radioactive materials. i.e. it is not possible to make Polonium Pellets with a reactor in the nether or have a reactor in the overworld and store waste in the nether.